The social determinants of health (SDOH) are conditions in the environment where people are born, live, learn, work, play, and age that affect their health and quality of life. Unlike genetics or medical care, the social conditions people face daily—such as economic stability, education, social support, and access to healthcare—have a profound impact on health outcomes. By understanding the social determinants of health, we can address the root causes of health disparities and work towards achieving health equity for all.
In this article, we will explore the various factors that contribute to the social determinants of health, how they affect individuals and communities, and what steps can be taken to mitigate their impact on public health.
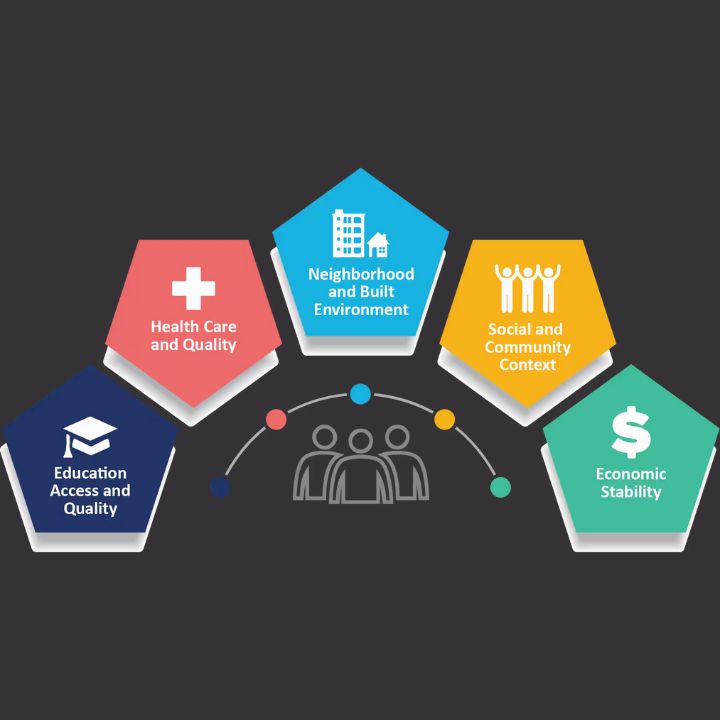
What Are Social Determinants of Health?
The social determinants of health are factors that go beyond an individual’s lifestyle choices and biology, extending to the environment and social conditions in which they live. These determinants can include:
Economic Stability: Income, employment status, and economic resources greatly influence an individual’s access to healthcare, nutrition, housing, and other essentials.
Education: Access to quality education can affect a person’s ability to get a good job, make informed health decisions, and live a long and healthy life.
Social and Community Context: Social relationships, networks, and a sense of belonging contribute to mental and physical health. Community support systems and social inclusion can be significant protective factors for health.
Health Care Access and Quality: Access to healthcare services and the quality of care received directly affect health outcomes. Preventive services, medical treatments, and health insurance availability all play a crucial role.
Neighborhood and Built Environment: The physical environment—including air and water quality, housing conditions, transportation options, and access to healthy food—greatly impacts health. Unsafe neighborhoods and limited access to green spaces or recreational facilities can have negative effects on well-being.
Cultural and Environmental Factors: Cultural beliefs, societal norms, and environmental conditions are other key aspects that shape health outcomes. These factors can influence lifestyle choices, social behaviors, and access to healthcare services.
How Social Determinants of Health Influence Health Outcomes
The social determinants of health directly shape an individual’s life expectancy, quality of life, and overall health. By impacting key areas such as income, education, and access to healthcare, these determinants can increase the risk of chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and mental health disorders. Here’s how different aspects of SDOH can affect an individual’s health:
Economic Stability and Health
Economic stability is one of the most influential social determinants of health. Conversely, those with lower incomes often experience higher rates of chronic illness, mental health issues, and even shorter life expectancy.
Financial stress also leads to poor mental health, unhealthy coping mechanisms (such as smoking or overeating), and lack of access to necessary medical treatments.
Education and Health
Education is another crucial factor among the social determinants of health. Higher educational attainment is linked to better health outcomes, including longer life expectancy and lower rates of disease. Educated individuals are more likely to engage in healthy behaviors, access medical care, and understand how to navigate health systems.
On the other hand, those with limited education may struggle to make informed health decisions, resulting in lower health literacy. Poor health literacy can prevent individuals from understanding medical instructions, adhering to treatment regimens, or identifying early signs of illness.
Social and Community Context
The relationships and networks we build within our communities also influence our health. Positive social interactions and supportive relationships act as a buffer against stress, reducing the risk of mental health problems, substance abuse, and chronic conditions like hypertension. Conversely, individuals who experience social isolation, discrimination, or a lack of social support are at higher risk for both physical and mental health issues.
Social determinants like family structure, access to support groups, and community engagement play a vital role in promoting well-being. Communities that have strong social ties and offer opportunities for interaction and engagement tend to have better health outcomes overall.
Healthcare Access and Quality
Access to affordable, quality healthcare is a fundamental social determinant’s of health. Regular access to preventive care, screenings, and vaccinations can reduce the risk of many diseases, while timely medical treatment for existing conditions can prevent complications and improve quality of life.
However, disparities in healthcare access remain a significant issue. People living in rural or underserved urban areas may have limited access to doctors, hospitals, and other medical facilities, which can delay diagnosis and treatment. Additionally, lack of insurance or high out-of-pocket costs often lead to underutilization of necessary healthcare services, exacerbating health inequities.
Neighborhood and Built Environment
Where people live matters when it comes to their health. The neighborhood and built environment encompass physical aspects like housing quality, transportation access, air and water quality, and proximity to parks or recreational spaces. Poorly designed or unsafe neighborhoods with limited access to public transportation, grocery stores, or healthcare facilities can have a detrimental effect on health.
Cultural and Environmental Factors
Cultural beliefs, societal norms, and environmental factors can either promote or hinder health behaviors. For example, in some cultures, specific dietary restrictions or practices may contribute to chronic health conditions like obesity or diabetes. Additionally, environmental hazards such as exposure to chemicals, pollution, and unsafe working conditions disproportionately affect marginalized populations, leading to negative health outcomes.
Addressing the Social Determinants of Health
Social Determinants of Health disparities and promote health equity, it’s essential to address the social determinants of health. This requires coordinated efforts across sectors—government, healthcare providers, schools, businesses, and communities—working together to improve living conditions and access to essential resources.
Community-Based Solutions
Local communities are often best positioned to address the social determinants of health. Community-based initiatives such as food banks, after-school programs, mental health services, and housing support can have a profound impact on improving health outcomes.
Community engagement and empowerment are key to creating lasting change. By building strong, supportive networks, communities can better address challenges like poverty, homelessness, and social isolation that negatively affect health.
Healthcare System Improvements
Improving the accessibility and quality of healthcare is another vital way to address the social determinants of health. This includes ensuring that everyone, regardless of income or background, has access to affordable healthcare services. Expanding telehealth, improving access to mental health care, and reducing healthcare costs are all essential steps toward closing the healthcare gap.
Final Thought of Social Determinants of Health
The social determinants of health are critical factors influencing the health and well-being of individuals and communities. By addressing these determinants, we can work toward reducing health disparities, improving overall health outcomes, and ensuring that all people have access to the resources they need to lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
Understanding how social determinants of health impact people’s lives is a crucial step in creating a healthier and more equitable society.


















